Bursitis
Find a doctorBursitis causes painful swelling around bones and joints. There are many types and causes of bursitis. At Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic, our orthopedic specialists offer advanced bursitis treatments to help you move better with less pain.
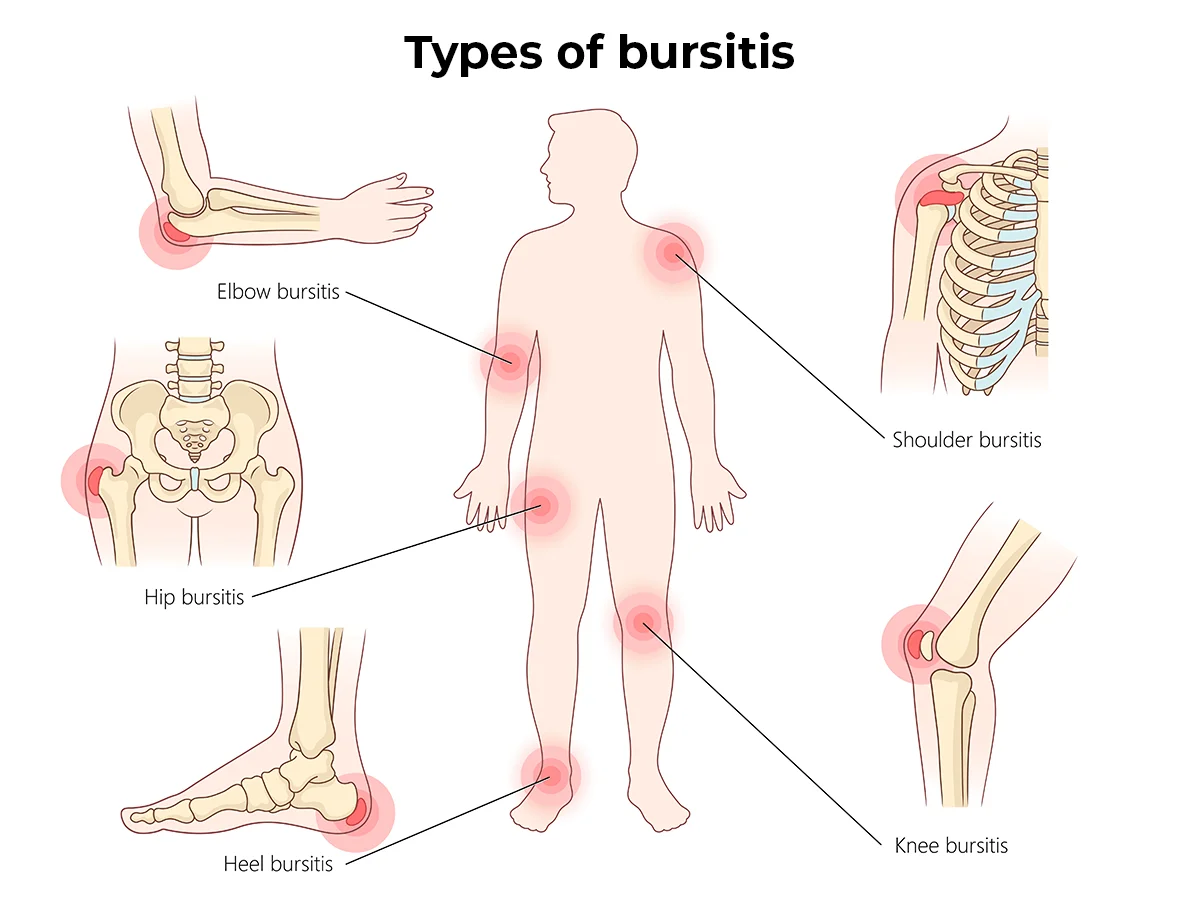
Bursitis can occur many different places.
What is bursitis?
Bursitis is an inflammatory condition that stems from swelling in small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae. Bursa sacs cushion the space between your bones and soft tissue, helping to reduce friction as your bones and joints move. Inflamed bursae can make movements painful.
Causes of bursitis
Bursitis is often an overuse injury. This means it results from frequent, repetitive movements. When these movements put pressure on a joint, they can irritate and inflame the bursae around that joint.
Other potential causes include:
- Arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis and gout
- Changes in activity levels, such as training for a marathon
- Infections
- Obesity
- Spine disorders
- Traumatic injury
Bursitis symptoms
Bursitis symptoms may vary depending on the disease type and affected part of the body. Common signs of bursitis include:
- Joint pain and tenderness, especially when you press on a joint or move it
- Red, warm skin over the joint
- Stiff, swollen joints
- Trouble bending and moving joints
Bursitis types
Inflammation can occur in bursae throughout your body. You’re most likely to develop bursitis in joints that have a lot of repetitive use or pressure. Common types of bursitis include:
- Butt (ischial) bursitis: Inflammation in the bursa that protects your sit bones (the bones you sit on) causes pain in the buttocks or backs of the thighs (hamstrings).
- Elbow (olecranon) bursitis: Bursa inflammation near an elbow joint causes elbow pain.
- Heel bursitis: Inflammation in a bursa between your heel bone and Achilles tendon causes heel, foot and/or ankle pain.
- Hip (trochanteric) bursitis: Inflammation in a bursa that covers the bony point of the hip bone causes hip pain.
- Knee (prepatellar) bursitis: An inflamed bursa in front of your kneecap (patella) causes knee pain.
- Shoulder (subacromial) bursitis: Inflammation in the bursae between your rotator cuff, tendons and shoulder blade causes shoulder pain.
Bursitis diagnosis
Your health care provider will look at your joints, ask about your symptoms and assess your range of motion during a physical exam. They may perform a tissue tension test, pressing on tendons and joints to find inflamed areas. In some cases, your provider may order a blood test or take a sample of joint fluid to check for infections that cause bursitis.
Doctors often use imaging tests, such as an MRI or ultrasound, to diagnose bursitis. While X-rays don’t show inflamed bursae, they can be helpful to rule out arthritis or other bone problems.
Bursitis risk factors
Your chances of developing bursitis increase with age. Other factors that can increase your risk include:
- Diabetes
- Hobbies, jobs or activities that require repetitive movements or pressure on your bursae
- Inflammatory arthritis, such as gout and rheumatoid arthritis
- Obesity
- Spine problems
Complications of bursitis
Chronic bursitis may lead to complications like:
- Depression
- High stress levels
- Loss of mobility, which can lead to disability and weight gain
Bursitis prevention
You can lower your chances of developing bursitis by protecting your joints. Actions that may help include:
- Avoiding repetitive joint movements if possible
- Being physically active to strengthen your muscles and protect your joints
- Lifting with your legs (not your back) when picking up or carrying heavy items
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Warming up and stretching before you exercise
- Wearing protective gear, such as kneepads, when doing activities that put pressure on your joints
Bursitis treatments
Taking a break from activities that put pressure on inflamed bursae often improves bursitis symptoms. Physical therapy can help improve your range of motion and flexibility once the pain subsides.
To relieve symptoms, you can also try:
- Applying warm and cold compresses to the affected area
- Elevating the affected area
- Modifying certain activities to ease pressure on inflamed bursae
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce swelling
- Wearing a brace, splint or sling to take pressure off the affected area
Orthopedic services
Personalized orthopedic care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.