Endocarditis
Find a doctorEndocarditis is an infection in your endocardium (the inner lining of your heart). The heart specialists at Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic provide expert care for endocarditis to treat the infection and help restore your health.
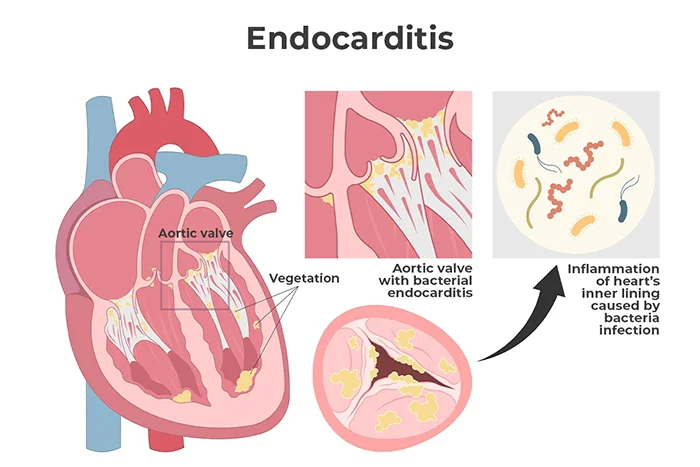
Bacterial endocarditis causes vegetations (lesions) on the inner lining of the heart.
What is endocarditis?
Endocarditis, also known as infective endocarditis or IE, occurs when the inner layer of your heart becomes infected. Usually, your immune system can fight off infections before they reach your heart. But if your endocardium is rough or damaged from heart disease or a heart defect, germs can attach to it and make you sick.
Endocarditis can damage your heart valves, leading to heart failure or stroke. But early treatment with the right antibiotics can help prevent these complications.
Causes of endocarditis
Endocarditis occurs when bacteria or fungi enter your bloodstream and travel to your heart. These germs can then infect your endocardium or your heart valves. Bacteria or fungi may get into your bloodstream from:
- Catheters or other medical devices that go through your skin, especially if you use one for a long period
- Dental procedures, especially if your teeth or gums are damaged
- Infections in other areas of your body, such as your gut or skin
- Intravenous (IV) drug use
Endocarditis symptoms
Symptoms of endocarditis can vary from person to person. They can also change over time in the same person and depend on the type of germ causing the infection. If you have endocarditis, you may experience:
- Blood in your urine
- Digestive issues, including nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite or upper abdominal pain
- Flu-like symptoms, such as body aches, chills, fatigue, fever and headache
- Heart murmur or a change in an existing heart murmur
- Painful red or purplish bumps that appear under the skin on your fingers or toes
- Painless, dark, flat spots on the palms of your hands or soles of your feet
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath or a cough that won't go away
- Swelling in your abdomen, legs or feet
- Tiny red spots under your fingernails, on the whites of your eyes, on your chest or inside your mouth
Endocarditis types
Types of infective endocarditis include:
- Acute IE, which comes on quickly and may cause serious complications within days
- Subacute or chronic IE, which develops over several weeks or months
- Prosthetic valvular IE, which develops within a year after a heart valve replacement
Endocarditis diagnosis
Your doctor diagnoses endocarditis by evaluating your symptoms, medical history and test results. Blood tests are often necessary. These tests check for signs of infection and inflammation.
Your doctor may also order heart imaging tests, such as:
- CT scan
- Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart)
- MRI
Endocarditis risk factors
Endocarditis is uncommon in people with healthy hearts. You have a higher risk of endocarditis if you have:
- Artificial heart valve
- Congenital (present at birth) heart condition
- Pacemaker or other medical device in your heart
- Structural heart disease
- Weakened immune system
Endocarditis prevention
If you are at risk of developing endocarditis, you can take action to help prevent the infection by:
- Avoiding body piercings, tattoos and IV drugs, which can allow germs into your bloodstream
- Brushing and flossing your teeth daily, and getting regular dental checkups
- Knowing the symptoms, and contacting your provider right away if you experience them
- Taking antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor before dental and medical procedures
Endocarditis treatment
Treatment for endocarditis may include:
- Antibiotics: Infective endocarditis usually requires IV antibiotics for two to six weeks. You may be hospitalized for all or part of this treatment.
- Surgery: If antibiotics alone cannot clear the infection, your provider may recommend heart surgery to remove infected tissue. If the infection damaged one or more of your heart valves, you may need surgery to repair or replace them.
Heart services
Personalized heart care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.