Esophageal cancer
Find a doctorAn esophageal cancer diagnosis can be stressful and overwhelming. The cancer specialists at Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic are here for you with leading-edge therapies and compassionate support.
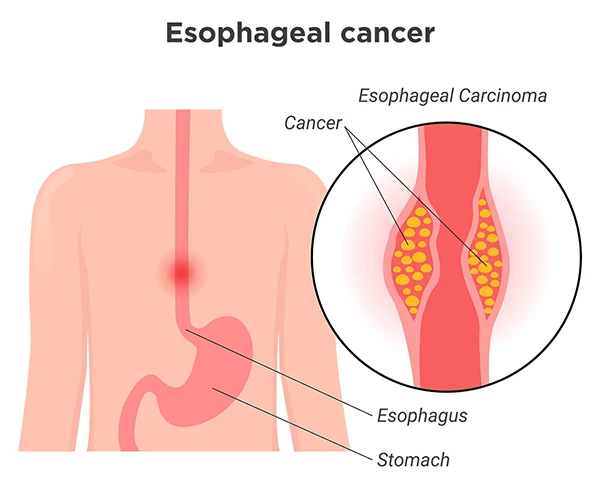
Esophageal cancer starts in the lining of the esophagus.
What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer affects your esophagus (the hollow tube that connects your throat to your stomach). This cancer starts in the lining of your esophagus and may spread to other layers as it grows.
Outcomes for esophageal cancer are better if treatment starts in the early stages. Depending on the type and stage, treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or immunotherapy.
Causes of esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer occurs when DNA in your esophageal cells mutates (changes). This change causes the cells to grow and divide out of control, forming a tumor.
Smoking or heavy alcohol use may trigger mutations in esophageal cells. In other cases, cell changes associated with esophageal cancer may run in families.
Esophageal cancer symptoms
Esophageal cancer may not cause symptoms in the early stages. But as the disease progresses, it may cause:
- Hoarseness and cough
- Indigestion and heartburn
- Pain behind your breastbone
- Painful or difficult swallowing
- Weight loss
Esophageal cancer types
The two most common types of esophageal cancer are:
- Adenocarcinoma, which starts in the cells of glands that produce mucus. This type often affects the lower part of the esophagus near your stomach.
- Squamous cell carcinoma, which starts in the thin, flat cells lining your esophagus. This is the most common type and usually affects the upper or middle section of your esophagus.
Esophageal cancer diagnosis
Diagnosing esophageal cancer usually involves a combination of a physical exam and tests. Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may recommend:
- Chest X-rays: These images help your doctor see your esophagus and other structures inside your chest.
- Barium swallow test: This test involves taking a series of X-rays of your esophagus and stomach after you drink a special liquid.
- Esophagoscopy: In this procedure, your doctor looks inside your esophagus using a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached to it. They may also do a biopsy, in which the doctor removes a tissue sample to examine in the lab.
Esophageal cancer risk factors
Some factors can make you more likely to develop esophageal cancer, including:
- Age of 65 or older
- Barrett's esophagus
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Heavy alcohol use
- Male sex assigned at birth
- Smoking or tobacco use
Esophageal cancer prevention
You can lower your risk of developing esophageal cancer if you:
- Avoid drinking alcohol
- Don't smoke
- Get proper treatment for GERD (if you have the condition)
Cancer services
Personalized cancer care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.