Gallstones
Find a doctorGallstones can cause severe pain, digestive upset, and even a life-threatening bile duct blockage. When you need treatment for gallstones, the gastroenterologists at Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic can help. We offer nonsurgical therapies and, if needed, partner with expert surgeons to provide gallbladder surgery.
What are gallstones?
Your gallbladder is a small organ that stores bile, a fluid made by your liver. If your bile doesn’t have the right amount of certain substances, it can harden into gallstones.
Gallstones can block a bile duct (a tube that connects your gallbladder and small intestine), causing a gallbladder attack. These attacks can be extremely painful and may be life-threatening in severe cases. Surgery to remove the gallbladder may be necessary.
Causes of gallstones
Gallstones form when your bile doesn’t contain the right balance of substances. People with gallstones typically have bile with:
- Not enough bile salts
- Too much bilirubin
- Too much cholesterol
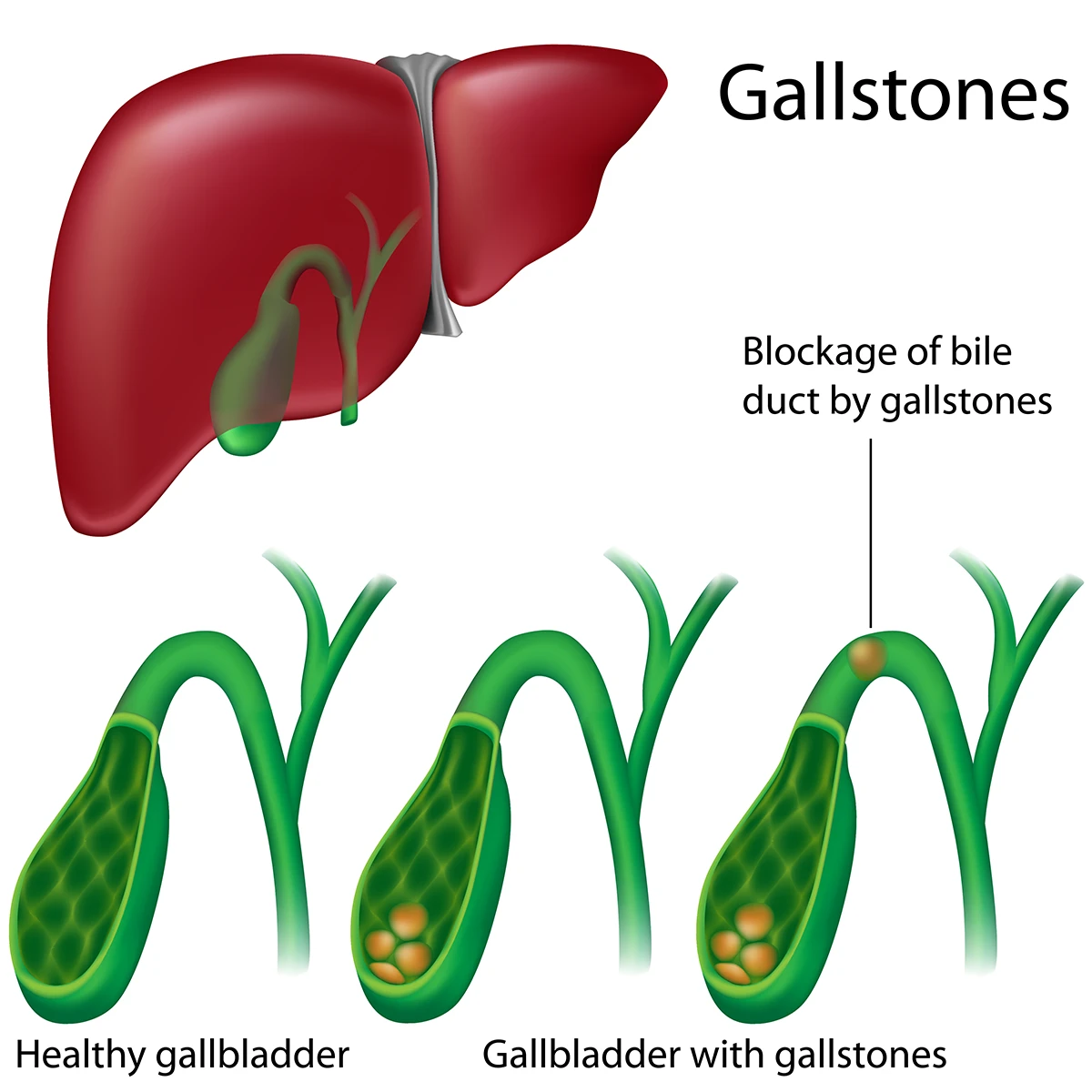
Gallstones form from bile and sometimes block the bile duct, causing a gallbladder attack
Gallstones symptoms
Small gallstones may not cause symptoms and are known as silent gallstones. But stones that block a bile duct may cause a gallbladder attack. The main symptom of a gallbladder attack is abdominal pain that:
- Is located in the upper right part of your abdomen under your rib cage
- Occurs after a heavy meal or at night
- Feels sharp or stabbing
If gallstones block a bile duct for more than a few hours, the pressure in your gallbladder increases. This pressure can damage your gallbladder, bile ducts or liver and requires immediate medical care. Signs of a severe gallbladder attack include:
- Abdominal pain that lasts more than two hours
- Fever or chills
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of your eyes)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tea-colored urine or pale stools
Gallstone types
The two types of gallstones are:
- Cholesterol stones: These arethe most common type. They are yellow-green and contain more than 50% cholesterol.
- Pigment stones: These stones are a dark color and contain bilirubin.
Gallstone diagnosis
Your doctor may diagnose gallstones by asking you about your symptoms and ordering tests. Tests for gallstones may include:
- Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation or infection in your gallbladder, liver or bile ducts
- Cholescintigraphy, an imaging test that uses a radioactive material to take pictures of your gallbladder and bile ducts
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), a procedure that uses endoscopy and X-rays to create images of your digestive tract
- Other imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI, to view your gallbladder and surrounding organs
Gallstone risk factors
You may be more likely to develop gallstones if you:
- Are female
- Are over age 40
- Have a family history of gallstones
- Have Native American or Mexican American ethnicity
- Have obesity
- Lose weight quickly or diet frequently
Gallstone prevention
You can help prevent gallstones by:
- Avoiding rapid weight loss or crash diets
- Eating a diet rich in fiber and healthy fats, and reducing sugar and processed foods
- Working toward or maintaining a healthy weight through healthy eating and regular exercise
GI services
Personalized gastrointestinal care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.