Osteoarthritis
Find a doctorOsteoarthritis causes swelling, pain and stiffness in your joints. The orthopedic specialists at Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic offer the latest osteoarthritis treatments to help you move with less pain.
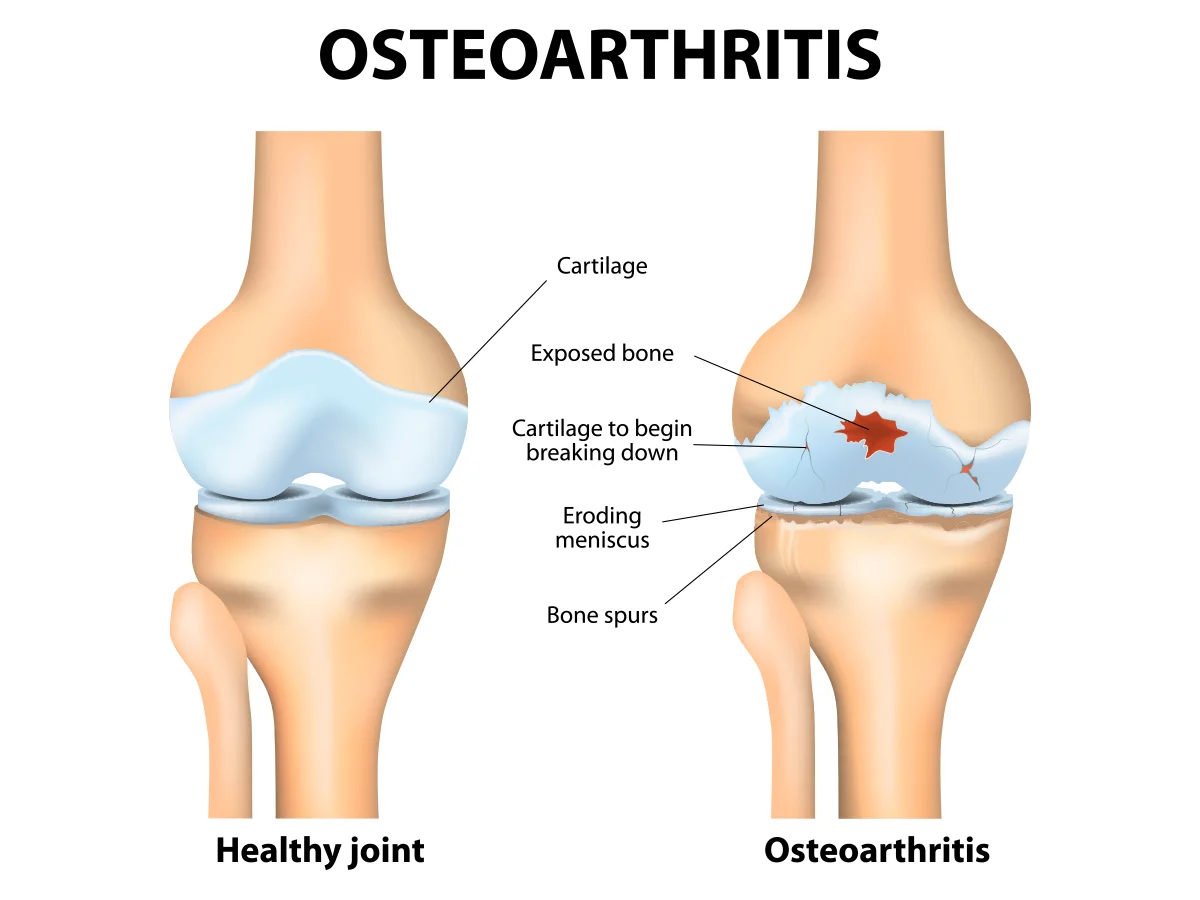
Osteoarthritis develops when the cartilage between the bones in your joints deteriorates and causes the bones to rub against each other, as shown on the right.
What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. It causes swelling, pain and stiffness in your joints, the places where your bones meet. This joint disease typically affects the joints in your hands, knees, hips and spine. Osteoarthritis can make it harder to bend and move the affected joints.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs when tissue called cartilage breaks down. This thin, rubbery tissue covers the ends of the bones in a joint, helping them glide and move. When cartilage wears away, your bones rub together. Over time, this friction can lead to painful, stiff joints.
Osteoarthritis symptoms
Osteoarthritis symptoms may vary depending on the affected joint. Common signs of osteoarthritis include:
- Back pain, hand pain, hip pain and/or knee pain
- Decreased range of motion
- Joint pain that’s often worse in the morning and eases throughout the day
- Joint pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest
- Rubbing, grating or crackling sensation when you move the joint
- Stiff joints, especially in the morning
- Swollen joints or a bump that forms over the affected joint
Osteoarthritis diagnosis
Your health care provider will examine your joints and assess your range of motion during a physical exam. They may bend a joint and listen for a crackling or grinding sound (called crepitation) that indicates osteoarthritis. They’ll also review your symptoms and medical history.
Your doctor may also order:
- Blood tests to rule out conditions that cause similar symptoms
- X-rays or other imaging tests to look for joint and cartilage damage
Osteoarthritis risk factors
People age 45 and older are most at risk of developing osteoarthritis. Other factors can also increase your risk, including:
- Bone fractures or joint injury
- Family history of arthritis
- Female sex assigned at birth
- Obesity
Complications of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can affect many aspects of your life. Severe joint pain may affect your ability to get around and complete daily tasks. As a result, you may develop complications like:
- Depression
- High stress levels
- Weight gain
Osteoarthritis prevention
Certain actions may lower your chances of developing osteoarthritis, such as:
- Avoiding repetitive joint movements
- Cutting back on inflammatory foods like red meat, sugary foods and drinks, and highly processed products
- Being physically active
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Wearing protective equipment when doing activities that can injure your joints
Osteoarthritis treatments
Nonsurgical treatments can ease osteoarthritis symptoms and improve mobility. These treatments include:
- Lifestyle changes, such as following an anti-inflammatory meal plan, staying physically active and managing your weight
- Oral anti-inflammatory medications to ease swelling and pain
- Physical therapy to improve joint mobility
- Steroid injections to ease pain and swelling
- Supportive devices like splints and braces
- Warm and cool compresses to soothe swollen, achy joints
- Complementary therapies like acupuncture
If severe osteoarthritis symptoms affect your ability to enjoy life, your doctor may recommend surgery. Surgical treatments for osteoarthritis include:
- Arthroscopy to remove damaged cartilage
- Joint fusion (arthrodesis) to permanently join two joint bones so they can’t rub together
- Joint replacement (arthroplasty) to replace a damaged joint with a prosthetic implant
- Osteotomy to realign bones and take pressure off joints
Orthopedic services
Personalized orthopedic care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.