Celiac disease
Find a doctorCeliac disease can damage your small intestine, leading to digestive problems and malnutrition. At Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic, our digestive disease specialists, also known as gastroenterologists, provide expert care so you can get the nutrients your body needs.
What is celiac disease?
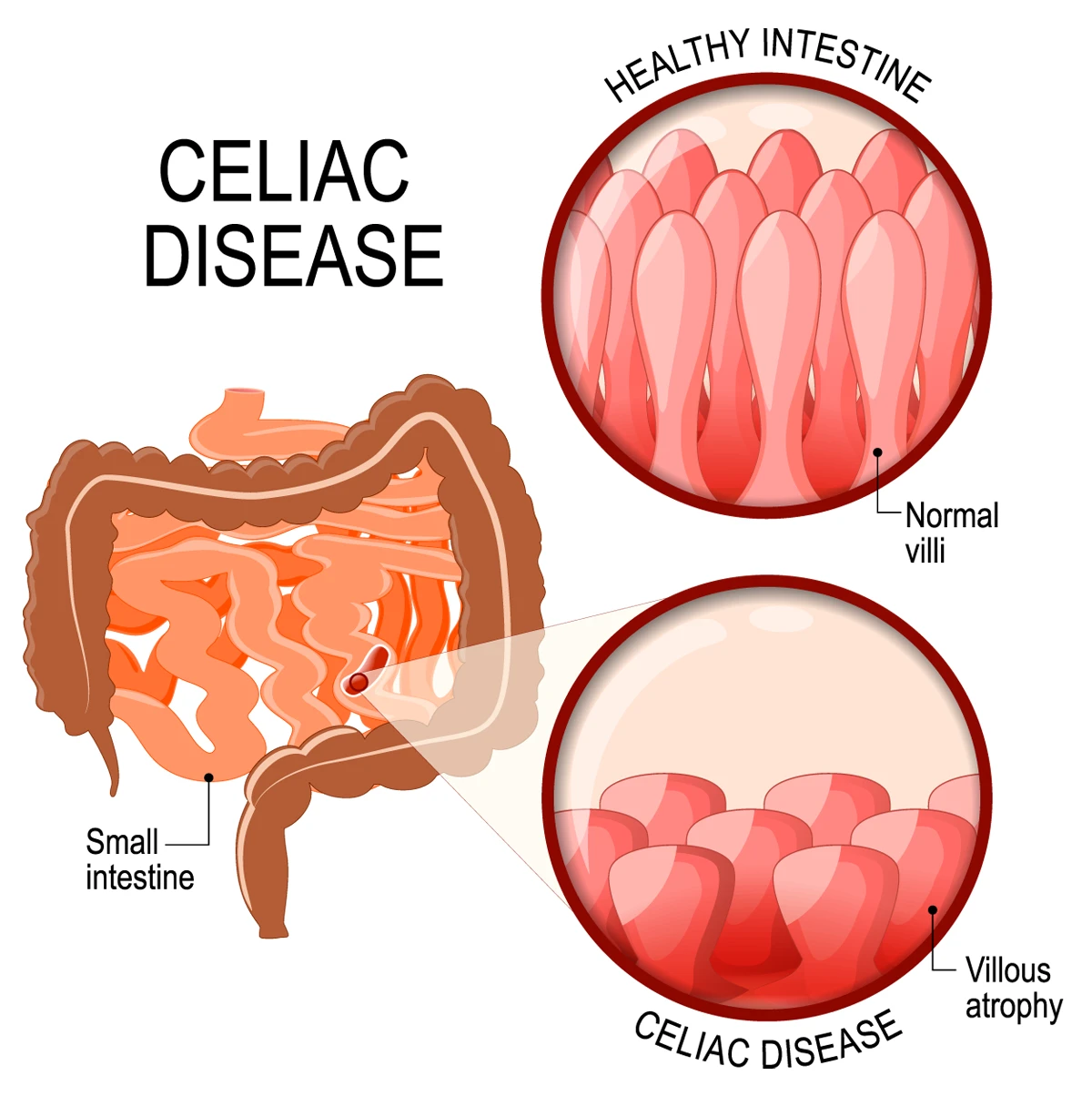
Celiac disease causes atrophy of the villi within the small intestine.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that damages your small intestine when you consume gluten. Gluten is a protein found in grains like barley, rye and wheat. Some medications, toothpastes and other products also contain gluten.
When you have celiac disease, your immune system sees gluten as a threat. It makes antibodies that attack gluten molecules. The resulting inflammation damages, and sometimes destroys, tiny fingerlike protrusions (villi) in the lining of your small intestine (mucosa).
Villi help your small intestine absorb nutrients from foods, which enter your bloodstream. When villi are damaged, it’s hard to get the nutrients your body needs, no matter how much food you eat.
Causes of celiac disease
A gene change (mutation) that runs in families causes most cases of celiac disease. But not everyone who inherits a changed gene develops this condition. Some people with celiac disease don’t have a known gene mutation.
In people with celiac disease, something triggers the immune system to start attacking gluten molecules. Examples of possible triggers include an infection, surgery or extreme stress. Experts aren’t sure why these triggers cause the body to react this way.
Celiac disease symptoms
Celiac disease affects people of all ages. Symptoms vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe.
Celiac disease symptoms in children
Infants and young children with celiac disease may have symptoms like:
- Behavioral changes, such as irritability, excessive clinginess or emotional withdrawal
- Digestive issues, such as abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea and constipation
- Failure to grow and gain weight
Celiac disease symptoms in teenagers
Teenagers with celiac disease may have:
- Delayed puberty or puberty that’s shorter than usual
- Dental problems
- Diarrhea, constipation or other digestive issues
- Hair loss
Celiac disease symptoms in adults
Digestive issues are less common in adults with celiac disease. Common celiac disease symptoms in adults include:
- Anemia
- Anxiety and/or depression
- Bone or joint pain
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Itchy, blister-like rash
- Missed menstrual periods
- Mouth sores
Celiac disease diagnosis
(Your doctor will order a blood test to diagnose celiac disease. You should continue to eat gluten products before the test. If you stop eating gluten, your body won’t make the antibodies the test looks for. A blood test can also show if you have low vitamin and mineral levels.
If a blood test indicates celiac disease, your doctor may perform other tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests include:
- Genetic testing (blood test) to check for gene changes that cause celiac disease
- Skin biopsy to diagnose dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin rash that often occurs with celiac disease
- Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy to view your small intestine and remove tissue to test for villi damage
Celiac disease risk factors
Certain factors can increase your chances of developing celiac disease, including:
- Autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis
- Chromosomal disorders, such as Down syndrome and Turner syndrome
- Family history of celiac disease
- Female sex assigned at birth
Complications of celiac disease
Celiac disease increases your risk of other health problems, including:
- Anemia
- Lactose intolerance
- Nervous system problems, such as peripheral neuropathy
- Reproductive system problems, such as missed periods or infertility
- Softening of your bones (osteoporosis or osteomalacia)
Celiac disease treatments
People with celiac disease should avoid foods, drinks, medications and other products that contain gluten. A gluten-free lifestyle can stop symptoms and give your small intestine time to heal. It also prevents additional intestinal damage. Your doctor may recommend supplements if blood tests show you have low nutrient levels.
GI services
Personalized gastrointestinal care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.