Coronary heart disease
Find a doctorCoronary heart disease affects blood flow to your heart, causing chest pain and increasing your risk of a heart attack. At Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic, our heart doctors offer advanced treatments to improve blood flow and protect your heart.
What is coronary heart disease (CHD)?
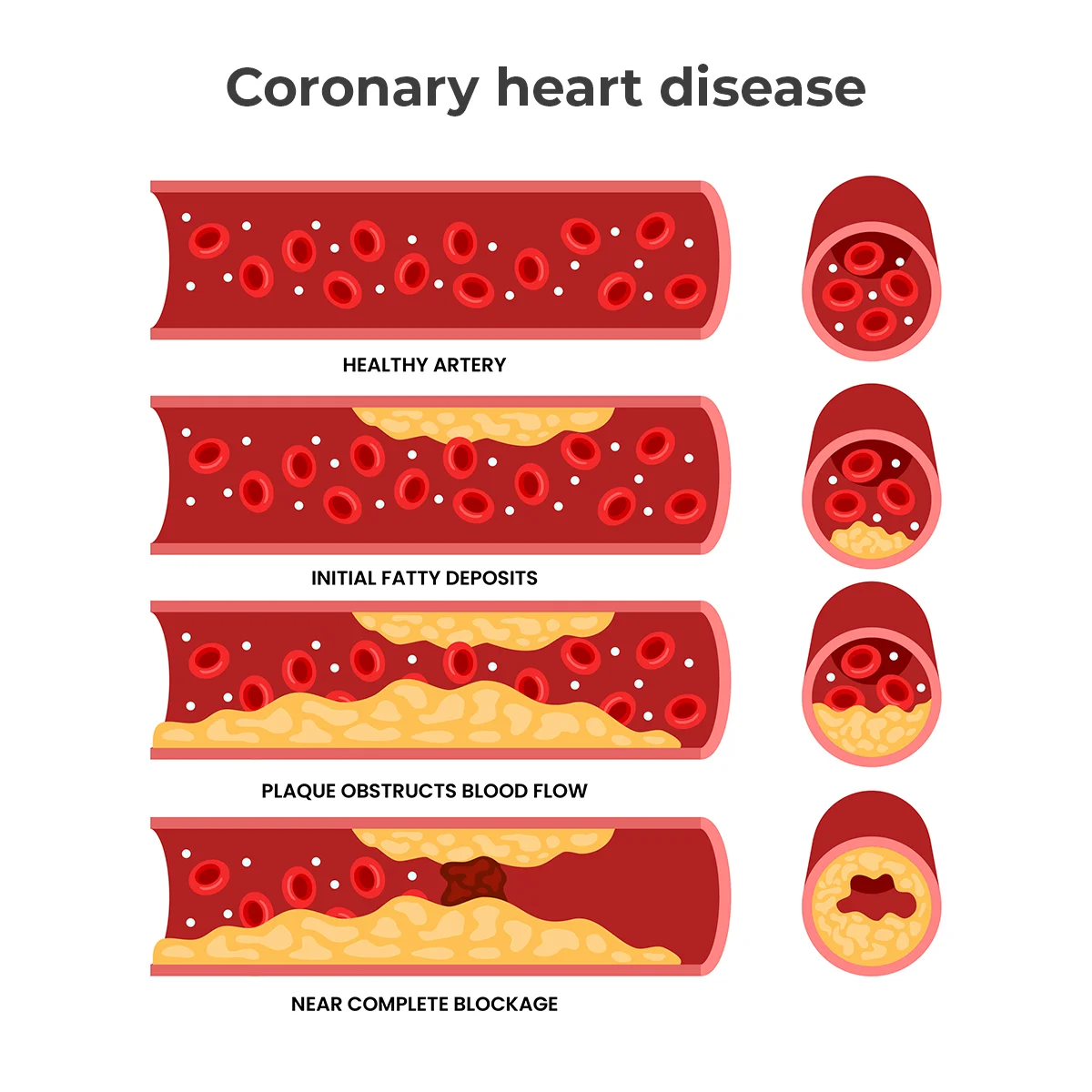
When you have coronary heart disease, plaque deposits in your arteries gradually get bigger and sometimes block the flow of blood.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) occurs when there’s a partial or complete blockage of blood flow in your heart’s coronary arteries. Your coronary arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to your heart. A blockage affects how much blood reaches your heart muscle, increasing your risk for chest pain (angina) and heart attack.
CHD is also called ischemic heart disease. Ischemic is the medical term for insufficient blood flow.
Causes of coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) causes coronary heart disease. CAD is a type of atherosclerosis that occurs when deposits of cholesterol (plaque) form inside your coronary arteries. As plaque builds up, the arteries become narrower and stiff. Blood then can’t flow as easily to your heart.
Coronary heart disease symptoms
CHD doesn’t always cause symptoms. Symptoms often appear as coronary arteries become narrower and less blood reaches your heart.
Chest pain or discomfort, known as angina, is the most common sign of CHD. You may feel a tightness, pressure, squeezing or burning in your chest. These sensations may spread to your shoulders, arms, jaw, neck or back. Chest pain is more likely to appear during physical activity and ease with rest.
Angina is a sign that your heart isn’t getting enough oxygen-rich blood. Chest pain, especially pain that doesn’t go away with rest or occurs with nausea, vomiting or shortness of breath, may be a sign of a heart attack. You should always seek medical attention right away for unexplained or sudden chest pain.
Coronary heart disease diagnosis
Your heart doctor (cardiologist) will conduct a physical exam and listen to your heart. They’ll ask about your symptoms, medical history and lifestyle.
To make an accurate CHD diagnosis, your doctor may order tests like:
- Coronary calcium scan to measure calcium inside your coronary arteries
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) to assess your heart rhythm and measure your heart’s electrical activity
- Imaging tests, such as a cardiac MRI, CT scan, positron emission tomography (PET) scan or angiogram, to assess heart damage and blood flow
- Stress test to assess heart function and blood flow while your heart beats fast
Coronary heart disease risk factors
Certain health conditions and other factors may increase your chances of developing CHD. These risk factors include:
- Addiction to alcohol, tobacco or other substances
- Age over 45 (males) or 55 (females)
- Atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease
- Diabetes
- Exposure to pollution, secondhand smoke and other toxins
- Family history of early heart disease (before 55 in males, 65 in females)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High LDL cholesterol levels or low HDL cholesterol levels
- High stress levels
- Obesity
Coronary heart disease prevention
Actions that may help lower your chances of developing CHD include:
- Cutting back on alcohol
- Finding healthy ways to manage stress
- Maintaining a healthy weight through physical activity and a heart-healthy diet
- Managing conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes
- Seeking help to quit smoking or using other substances
Complications of coronary heart disease
CHD increases your risk of heart problems such as:
- Arrhythmia
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Sudden cardiac arrest
Coronary heart disease treatments
CHD treatments depend on disease severity and your unique diagnosis. Treatment options may include:
- Medications to lower blood pressure, cholesterol and triglycerides
- Nitrate medications to open up coronary arteries and ease angina
- Heart procedures to open narrowed coronary arteries, such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Heart services
Personalized heart care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.