Eczema
Find a doctorEczema is a noncontagious skin condition that causes areas of dry, itchy skin. At Atrium Health Floyd and Harbin Clinic, our internal medicine specialists offer proven therapies to treat the symptoms of eczema and help you prevent future flare-ups.
What is eczema?
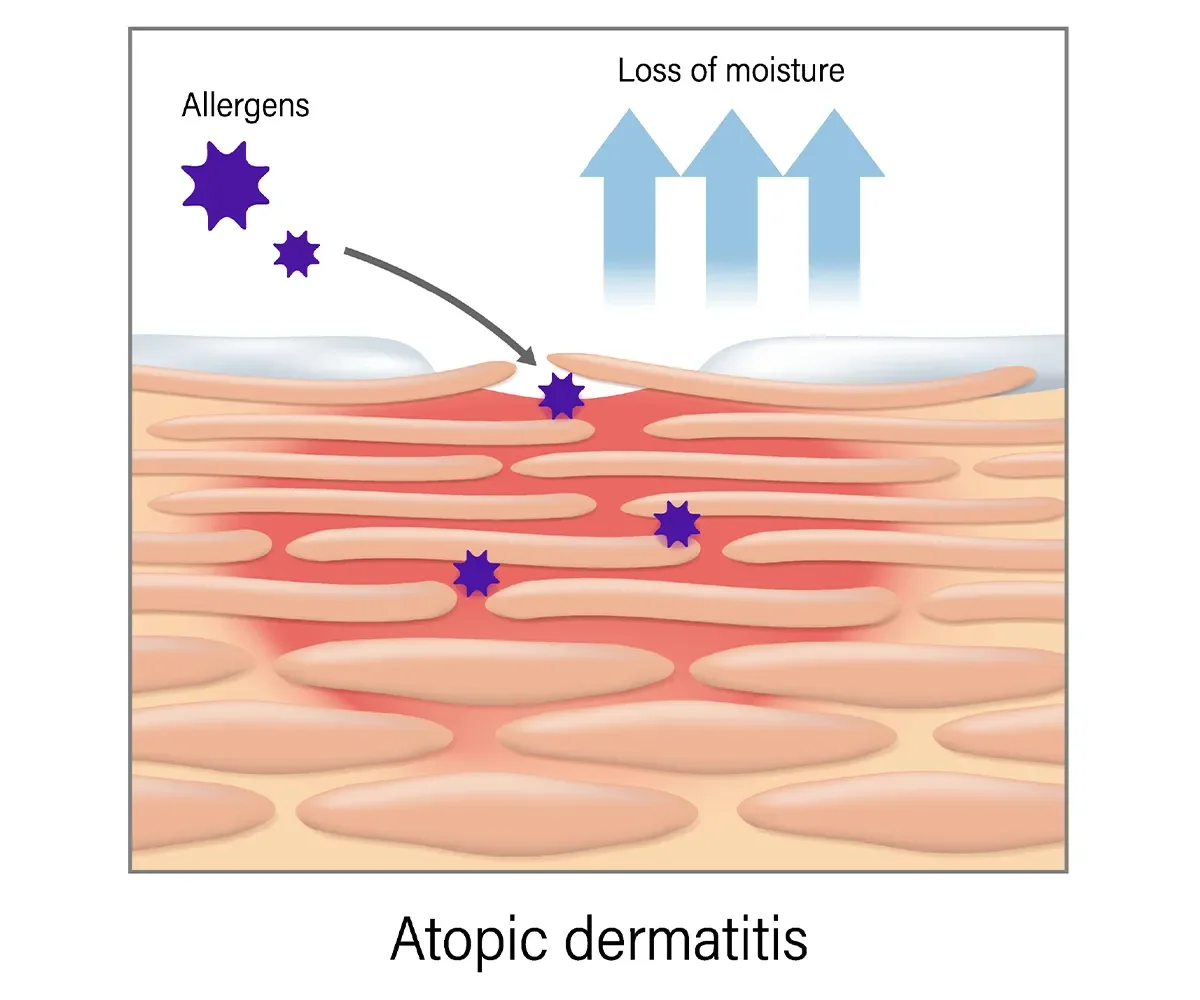
One way that eczema occurs is when allergens contribute to symptoms.
Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that affects about 10% of the U.S. population. This condition is more common in children and adolescents than in adults, with symptoms usually appearing before the age of 5. Many people outgrow eczema as they reach adulthood.
Eczema is more than just itchy skin. This condition can be severe enough to interfere with your daily activities. It may also cause broken skin, which increases your risk of infection. Fortunately, proper treatment and home care can help relieve symptoms and decrease your risk of complications.
Causes of eczema
Experts don't know exactly what causes eczema. But a combination of genetic and environmental factors likely play a role.
If you have eczema, certain things can trigger a flare-up (increase in symptoms), including:
- Allergens such as dust mites, mold and pollen
- Cold or dry air
- Emotional stress
- Frequent baths or showers, especially if you don't apply moisturizer afterward
- Foods you are allergic to
- Infections, including colds or flu
- Irritants such as chemicals, dyes, fragrances or rough fabrics
Eczema symptoms
The most common symptom of eczema is a dry rash that may be:
- Itchy
- Red or darkened
- Scaly or crusty
Symptoms may flare up and then resolve in a cycle. Your skin may begin to feel itchy before the rash appears. Scratching can make the rash worse and cause the skin to crack, thicken or weep clear fluid.
An eczema rash can appear anywhere on the body, but its location may vary depending on your age. Adults with eczema often develop a rash on the insides of their elbows and knees. They may also experience flare-ups on their hands, feet and neck.
Babies often get the first signs of eczema on their face and chin. As they grow, they may develop patches of eczema on their arms, legs, hands and neck. Some children see an improvement in symptoms for several years but experience a flare-up during puberty. Hormones, stress and harsh skin care products may lead to this change.
Eczema diagnosis
Doctors often diagnose eczema with a physical exam and a discussion about symptoms and family history. When needed, they may perform a biopsy (take a small sample of skin) to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. If your doctor suspects allergies could be triggering your eczema symptoms, they may recommend allergy skin testing.
Eczema risk factors
Eczema is related to other allergic conditions. You are more likely to develop eczema if you or your parents have:
- Asthma
- Food allergies
- Hay fever (nasal allergies)
Eczema prevention
There is no known way to prevent eczema, but you can help avoid flare-ups by:
- Following your doctor’s treatment plan and using medications as prescribed
- Keeping your fingernails short to avoid damaging the skin
- Knowing your triggers and avoiding them whenever possible
- Moisturizing your skin frequently, especially after bathing
- Taking shorter, cooler baths and showers
- Using fragrance-free, dye-free skin products and laundry detergent
Eczema treatment
Treatment for eczema depends on your age and medical history along with the severity of your condition. Your treatment options may include:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can help relieve itching and allergies that may trigger eczema.
- Frequent moisturizing: Using fragrance-free, dye-free, gentle cleansers and moisturizers may treat minor flare-ups. You can also apply an ointment such as petroleum jelly two to three times a day.
- Humidifier: Using a humidifier if your indoor air is dry can help relieve symptoms.
- Hydrocortisone products: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams can calm itching, inflammation and redness.
- Prescription medications: Your provider may prescribe medications to treat severe eczema flares and prevent new ones. Options include topical and oral corticosteroids, biologics and immunosuppressants.
Dermatology
Personalized dermatology care from experts you trust
Get the MyAtriumHealth app
Get test results, message your provider & more.